High Level Overview
Kamaji is an open source Kubernetes Operator that transforms any Kubernetes cluster into a Management Cluster capable of orchestrating and managing multiple independent Tenant Clusters. This architecture is designed to simplify large-scale Kubernetes operations, reduce infrastructure costs, and provide strong isolation between tenants.
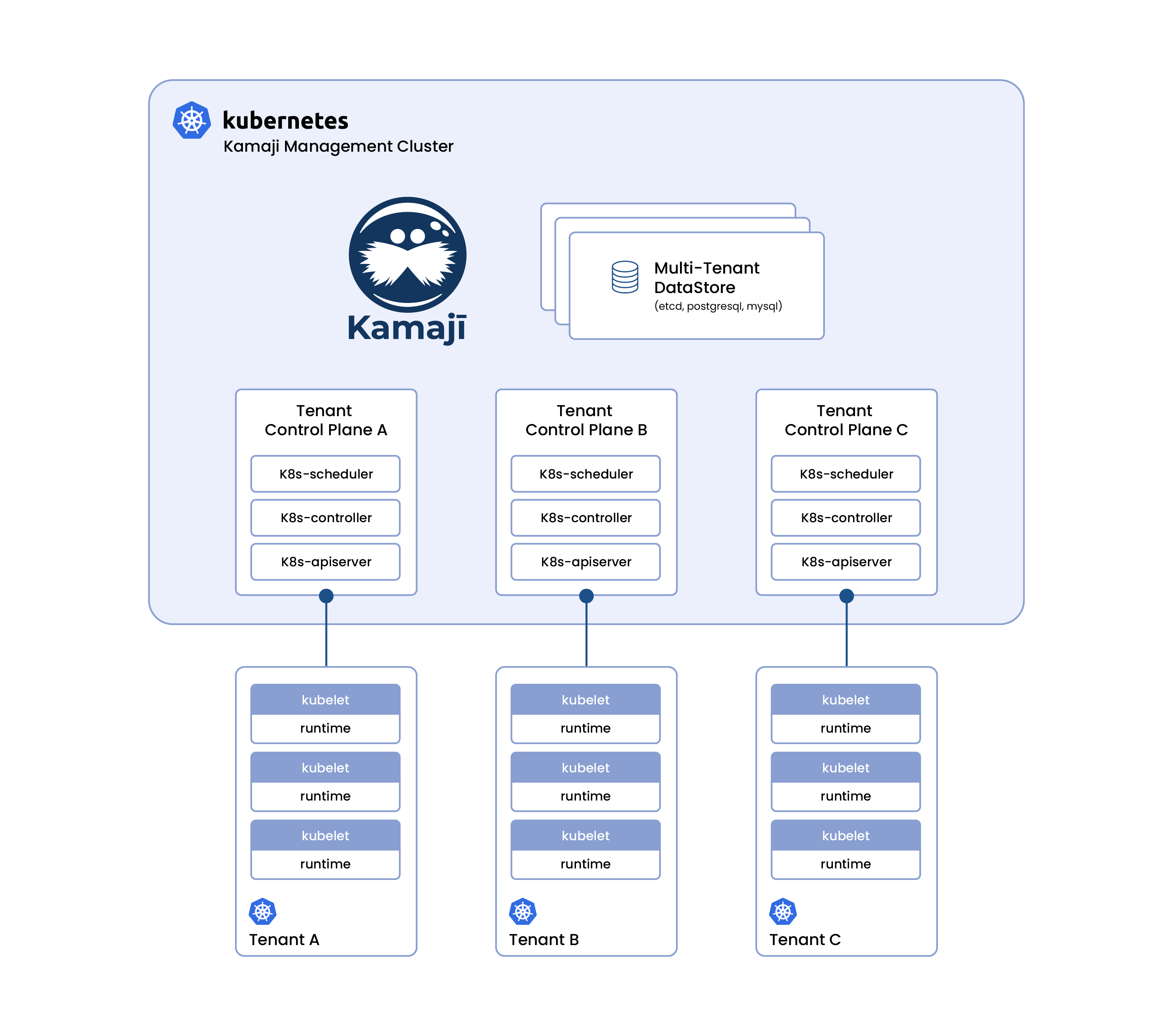
Architecture Overview
-
Management Cluster:
The central cluster where Kamaji is installed. It hosts the control planes for all Tenant Clusters as regular Kubernetes pods, leveraging the Management Cluster’s reliability, scalability, and operational features. -
Tenant Clusters:
These are user-facing Kubernetes clusters, each with its own dedicated control plane running as pods in the Management Cluster. Tenant Clusters are fully isolated from each other and unaware of the Management Cluster’s existence. -
Tenant Worker Nodes:
Regular virtual or bare metal machines that join a Tenant Cluster by connecting to its control plane. These nodes run only tenant workloads, ensuring strong security and resource isolation.
Design Principles
-
Unidirectional Management:
The Management Cluster manages all Tenant Clusters. Communication is strictly one-way: Tenant Clusters do not have access to or awareness of the Management Cluster. -
Strong Isolation:
There is no communication between different Tenant Clusters. Each cluster is fully isolated at the control plane and data store level. -
Declarative Operations:
Kamaji leverages Kubernetes Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) to provide a fully declarative approach to managing control planes, datastores, and other resources. -
CNCF Compliance:
Kamaji uses upstream, unmodified Kubernetes components and kubeadm for control plane setup, ensuring that all Tenant Clusters follow CNCF Certified Kubernetes Software Conformance and are compatible with standard Kubernetes tooling.
Extensibility and Integrations
Kamaji is designed to integrate seamlessly with the broader cloud-native and enterprise ecosystem, enabling organizations to leverage their existing tools and infrastructure:
-
Infrastructure as Code:
Kamaji works well with tools like Terraform and Ansible for automated cluster provisioning and management. -
GitOps:
Kamaji supports GitOps workflows, enabling you to manage cluster and tenant lifecycle declaratively through version-controlled repositories using tools like Flux or Argo CD. This ensures consistency, auditability, and repeatability in your operations. -
Cluster API Integration:
Kamaji can be used as a Cluster API Control Plane Provider, enabling automated, declarative lifecycle management of clusters and worker nodes across any infrastructure. -
Enterprise Addons:
Additional features, such as Ingress management for Tenant Control Planes, are available as enterprise-grade addons.
Learn More
Explore the following concepts to understand how Kamaji works under the hood:
Kamaji’s architecture is designed for flexibility, scalability, and operational simplicity, making it an ideal solution for organizations managing multiple Kubernetes clusters at scale.